Formation and Properties of Chitosan-Cellulose Nanocrystal Polyelectrolyte-Macroion Complexes for Drug Delivery Applications
Authors:
Hezhong Wang and Maren Roman
Affiliation:
Macromolecules and Interfaces Institute and Department of Wood Science and Forest Products, Virginia Tech, Blacksburg, Virginia 24061, United States
Description:
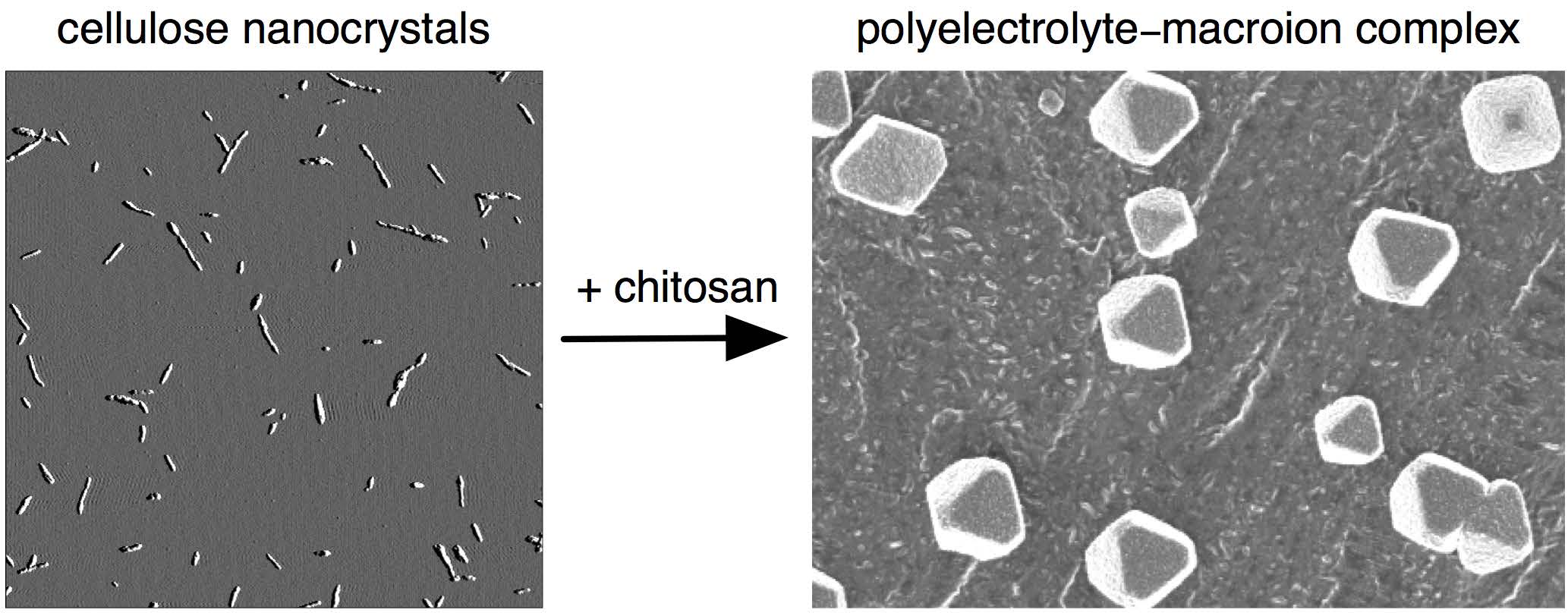
This study examines a novel polyelectrolyte-macroion complex (PMC) between chitosan, a cationic polysaccharide, and cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs), anionic, cylindrical nanoparticles, for potential applications in drug delivery. CNCs were prepared by H2SO4 hydrolysis of wood pulp. The formation of PMCs was monitored by turbidimetric titration. In titrations of a chitosan solution with a CNC suspension, the turbidity reached a plateau, but it had a maximum and then decreased when the direction of titration was reversed. PMC particles were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, dynamic light scattering, and laser Doppler electrophoresis. The particles were composed primarily of CNCs and ranged in size from a few hundred nanometers to several micrometers, depending on the cellulose/chitosan ratio. Particles formed at amino/sulfate group molar ratios >1 were nearly spherical in shape and positively charged, whereas particles formed at ratios <1 had well-defined nonspherical shapes and were negatively charged.
Publications:
- Wang, Hezhong, and Maren Roman; Formation and Properties of Chitosan-Cellulose Nanocrystal Polyelectrolyte-Macroion Complexes for Drug Delivery Applications; Biomacromolecules, 2011
Tags:
CelluloseRelated Chronicles:
No related chronicles available
Files:
| File Name | File Description | File Type | File Size | File URL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FTIR data (Figure 6) | Excel file with the raw FTIR data shown in Figure 6 of the publication | xlsx | 141.33 KB | Login to download |